Earth VS Jupiter – A Battle Against Time
Earth VS Jupiter – A Battle Against Time
A Battle Against Time.
The concept of time is not absolute, but rather is influenced by various factors, especially gravity, as described by Einstein’s theory of General Relativity. Gravity causes time to “dilate,” or move at different rates depending on the gravitational field’s strength. This means that the stronger the gravitational field, the slower time passes relative to a weaker gravitational field.
Let’s break this down in the context of two clocks, one on Earth and one on Jupiter, which have different gravitational fields due to their varying masses and radii.
1. Gravitational Time Dilation:
- General Relativity tells us that time passes more slowly in stronger gravitational fields. This means that a clock closer to a massive object (in a stronger gravitational field) will tick more slowly compared to a clock that is further away or in a weaker gravitational field.
- The formula for gravitational time dilation is derived from General Relativity and can be approximated as:
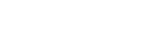
- Δt0 is the time interval in the absence of gravity (or far from the gravitational source),
- G is the gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field,
- r is the distance from the center of the object,
- c is the speed of light.
The closer the clock is to the massive object (in this case, Earth or Jupiter), the more significant the time dilation effect.
2. Gravitational Strength on Earth vs Jupiter:
- Earth’s Gravity:
- The gravitational acceleration on Earth is approximately
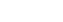
- Earth has a mass of about
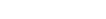 and a radius of about
and a radius of about 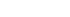
- Given these values, the gravitational field on Earth’s surface is weaker than Jupiter’s.
- The gravitational acceleration on Earth is approximately
- Jupiter’s Gravity:
- Jupiter’s gravitational acceleration is much stronger at about
 due to its much larger mass.
due to its much larger mass. - Jupiter has a mass of about
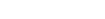 and a radius of about
and a radius of about 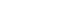 making its gravitational field significantly stronger than Earth’s.
making its gravitational field significantly stronger than Earth’s.
- Jupiter’s gravitational acceleration is much stronger at about
The key point here is that the gravitational potential on Jupiter’s surface is stronger, meaning that a clock on Jupiter would experience greater gravitational time dilation than a clock on Earth.
3. Time Dilation Effect in Practice:
- In a stronger gravitational field, such as Jupiter’s, time passes slower relative to a weaker gravitational field, like Earth’s. This means that the clock on Jupiter would tick slower than the clock on Earth.
Using the formula for time dilation, we can estimate the difference in time passage between Earth and Jupiter.
4. Comparison of Clocks:
- Time on Earth:
- The gravitational time dilation effect on Earth is relatively small, but measurable over long periods. However, over short periods like hours or days, the difference is negligible.
- Time on Jupiter:
- Jupiter’s gravity causes a much stronger dilation effect. A clock on Jupiter would run slower than a clock on Earth.
To quantify the difference:
- The gravitational potential at the surface of Earth and Jupiter can be calculated.
- Using Earth’s parameters, we find the time dilation factor on Earth to be very small (only slightly slower than an identical clock far from any mass).
- For Jupiter, the stronger gravitational field would result in a noticeably larger time dilation effect.
Even though the effect is small, in the moment, if we were able to monitor the clocks simultaneously, we would observe the clock on Jupiter running more slowly than the one on Earth.
5. Real-World Example:
If we assume both clocks are synchronized (e.g., using signals far from any massive body), then:
- After some time has passed, let’s say a day, the clock on Jupiter would show a slightly shorter elapsed time compared to the clock on Earth.
- If we were monitoring them continuously, the time on the Earth clock would be ticking faster than on Jupiter’s clock, because the stronger gravity on Jupiter slows the passage of time relative to Earth.
For instance, after one day (86,400 seconds):
- The difference between the two clocks might be on the order of milliseconds or even microseconds, but this gap would accumulate over longer periods. Over a year, this difference becomes more noticeable.
A Battle Against Time:
In the moment, if you were to monitor two identical clocks, one on Earth and one on Jupiter, you would see the clock on Jupiter running slower due to the stronger gravitational field there. The clock on Earth, in the weaker gravitational field, would tick slightly faster, but the difference is small over short periods. Over long periods, however, the cumulative time difference would become significant.
