Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner
Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner: Ensuring Your Mail Server’s Security
In today’s digital landscape, securing your mail server against vulnerabilities is paramount. A compromised mail server can expose your domain to hackers, increase the risk of spam, and even lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information. Our Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner is a powerful tool designed to help administrators assess their email systems for potential weaknesses, ensuring a robust defense against cyber threats.
What is a Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner?
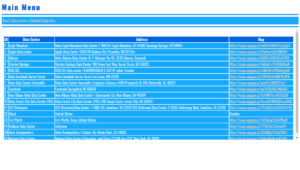
A Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner is a specialized application used to monitor and analyze mail servers for various security risks and vulnerabilities. This includes identifying issues like open relay, weak configurations, and possible exploits that hackers could use to compromise the server. The tool is intended to be used by professionals and legal entities who wish to protect their infrastructure and ensure their email systems are secure.
Key Features and Uses
- SMTP Vulnerability Checks
The scanner tests for common vulnerabilities in the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) settings, including the potential for an open relay. An open relay allows unauthorized users to send emails through your server, turning it into a spam distributor. By identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities, you can prevent your server from being exploited by hackers. - Domain Mail and Configuration Audits
It checks the configurations of domain mail setups, ensuring they are correctly structured and secure. This includes verifying settings such as DNS records, SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks. - Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
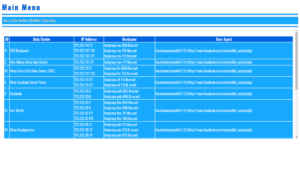
The scanner can continuously monitor your mail server for vulnerabilities, providing real-time alerts and actionable insights. This allows you to act swiftly and address any issues before they can be exploited. - Security Reporting and Defensive Measures
After scanning, the application generates a detailed report outlining any vulnerabilities found along with recommendations for defensive measures. This empowers administrators to implement the appropriate patches and security configurations, protecting the server from attacks.
How to Use the Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner
- Install the Application
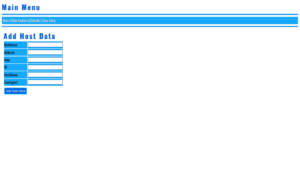
Download and install the Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner from our official website. The tool is designed for ease of use, with a user-friendly interface for seamless setup. - Enter Your Domain Details
Once installed, enter your mail server’s domain information and SMTP configurations. The scanner will automatically begin analyzing your mail server for vulnerabilities. - Run the Scan
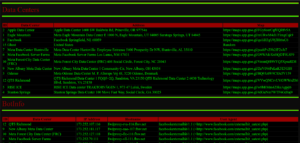
Click on the “Run Tests” button to initiate the vulnerability check. The scanner will systematically assess the server for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. - Review the Report
After the scan completes, review the detailed report provided by the application. This report will highlight any potential weaknesses along with step-by-step guidance on how to fix them. - Implement Security Recommendations
Based on the findings, apply the necessary changes and updates to your mail server’s configuration. This may include closing open relays, adjusting authentication protocols, or updating software versions.
Disclaimer
This application is intended for professional and legal use only. Unauthorized use of this tool on mail servers you do not own or have explicit permission to test could be illegal and result in severe consequences. Always ensure that you have the appropriate authorization before using the Mail Server Vulnerability Scanner on any server.
By using this tool responsibly, you can enhance the security and integrity of your email systems, making them more resistant to potential threats from hackers.