VoidCrawler File Reconnaissance 2.0.1
VoidCrawler
VoidCrawler File Reconnaissanceis 2.0.1 is a DaRK-themed, tactical directory intelligence system built for precision, stealth, and control.
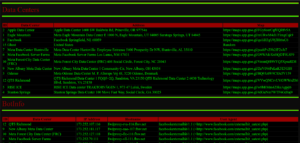
It recursively scans a base folder, renders a collapsible directory tree, and exposes direct-download links while filtering common web-app clutter.
VoidCrawler works exceptionally well with many DaRK Utilities.
Overview
VoidCrawler is designed as a reconnaissance tool rather than a general-purpose file manager. It strips noise, surfaces operational files, and presents a minimal, militarized UI ideal for server ops, forensic mapping, and admin dashboards.
Key Capabilities
- Recursive directory mapping with natural sort
- Collapsible folder UI (Bootstrap-powered)
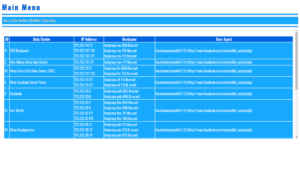
- Dedicated top-level “Direct Downloads” console
- Filters out
.htaccess,*.php,*.html,*.db,*.png - Pure PHP — no heavy frameworks required
History
VoidCrawler was not built to politely index.
It was not built to tag, catalog, or maintain compliance.
VoidCrawler was designed to invade.
To descend into dark directories.
To crawl the void between folders where broken paths hitchhike and dead files linger.
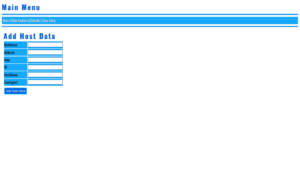
Installation
- Create a folder on your server for VoidCrawler (example:
/var/www/html/voidcrawler). - Drop the VoidCrawler PHP file (index.php) into that folder.
- Ensure the webserver user has read permissions:
chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/voidcrawler - Open the folder in a browser:
https://yourdomain.com/voidcrawler/
Quick Usage
The script scans from the directory it lives in by default. To change start path, edit the $root variable in the PHP file.
// default in index.php
$root = './';
$pathLen = strlen($root);
myScanDir($root, 0, strlen($root));
To scan elsewhere:
$root = '/var/www/data/archives/';How It Works
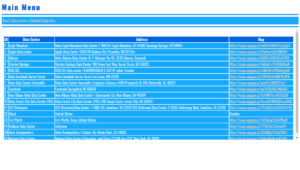
At its core, VoidCrawler uses a recursive function to enumerate entries, separate directories and allowed files, sort them naturally, and render them into two main UI blocks:
- Directories: a collapsible list on the left
- Direct Downloads: top-level file console for quick retrieval
Core recursive logic (excerpt)
function myScanDir($dir, $level, $rootLen)
{
global $pathLen;
if ($handle = opendir($dir)) {
$allFiles = [];
while (false !== ($entry = readdir($handle))) {
if ($entry != "." && $entry != ".." && $entry != ".htaccess") {
if (is_dir($dir . "/" . $entry)) {
$allFiles[] = "D: " . $dir . "/" . $entry;
} else if (!in_array(strtolower(pathinfo($entry, PATHINFO_EXTENSION)), ['php', 'html', 'db', 'png'])) {
$allFiles[] = "F: " . $dir . "/" . $entry;
}
}
}
closedir($handle);
natsort($allFiles);
// ...output folders and files with collapse UI...
}
}Configuration
Excluded Extensions
Default filter list (edit in the script):
['php', 'html', 'db', 'png']Path
Set the scanning root in the PHP file. Use absolute paths when moving outside webroot. Example:
$root = '/var/www/html/wp-content/uploads/';Security & Deployment Notes
- Do not expose VoidCrawler on a public route without authentication — it reveals directory structure.
- Restrict access via server auth or IP filtering when running in production.
- Use absolute paths to limit scan scope.
Changelog
- 2.1.0 — Branding overhaul, UI polish, DaRK theme applied.
- 2.0.x — Core scanning functions hardened (EvilMapper lineage).
License
MIT License (use, modify, distribute). Attribution appreciated when used in public-facing tools.
Copyright (c) 2025 K0NxT3D
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "VoidCrawler"), to deal
in the VoidCrawler without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies
of the VoidCrawler, and to permit persons to whom the VoidCrawler is furnished
to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the VoidCrawler.