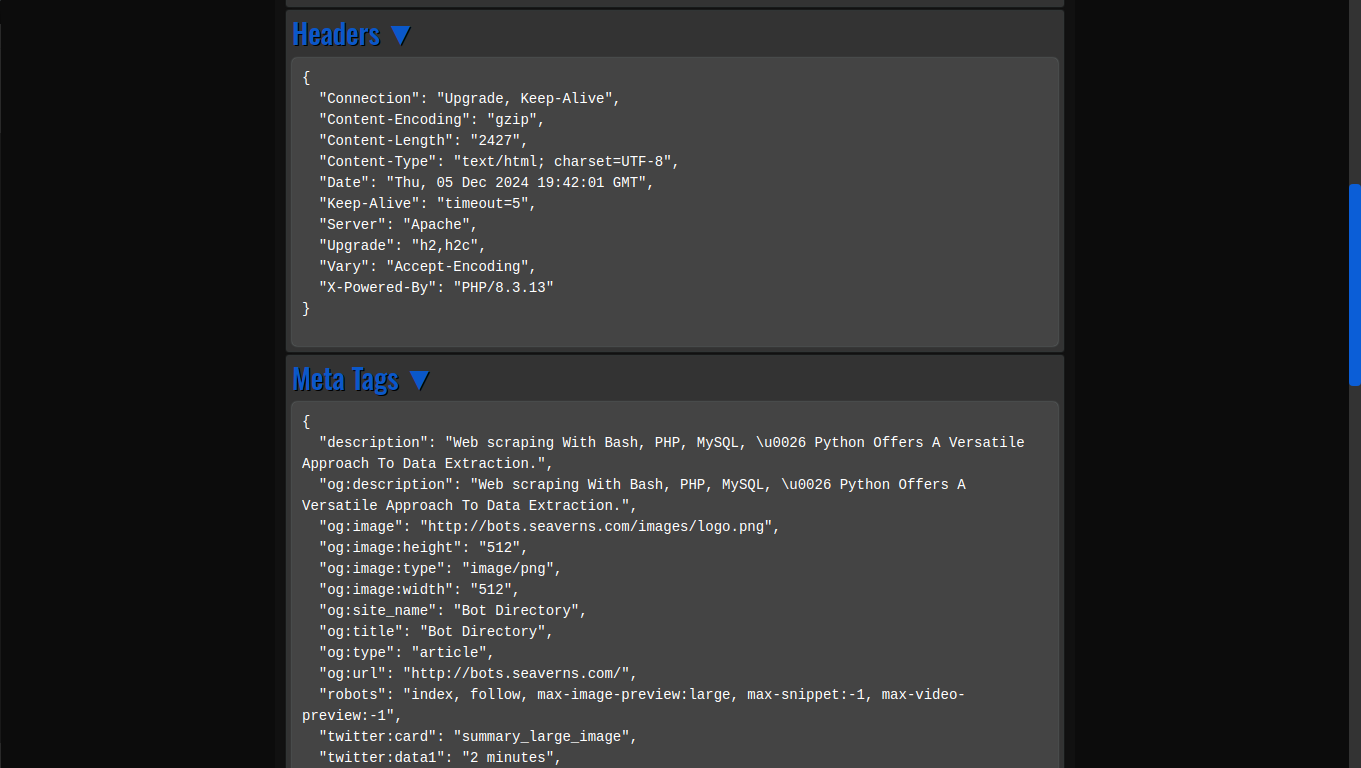
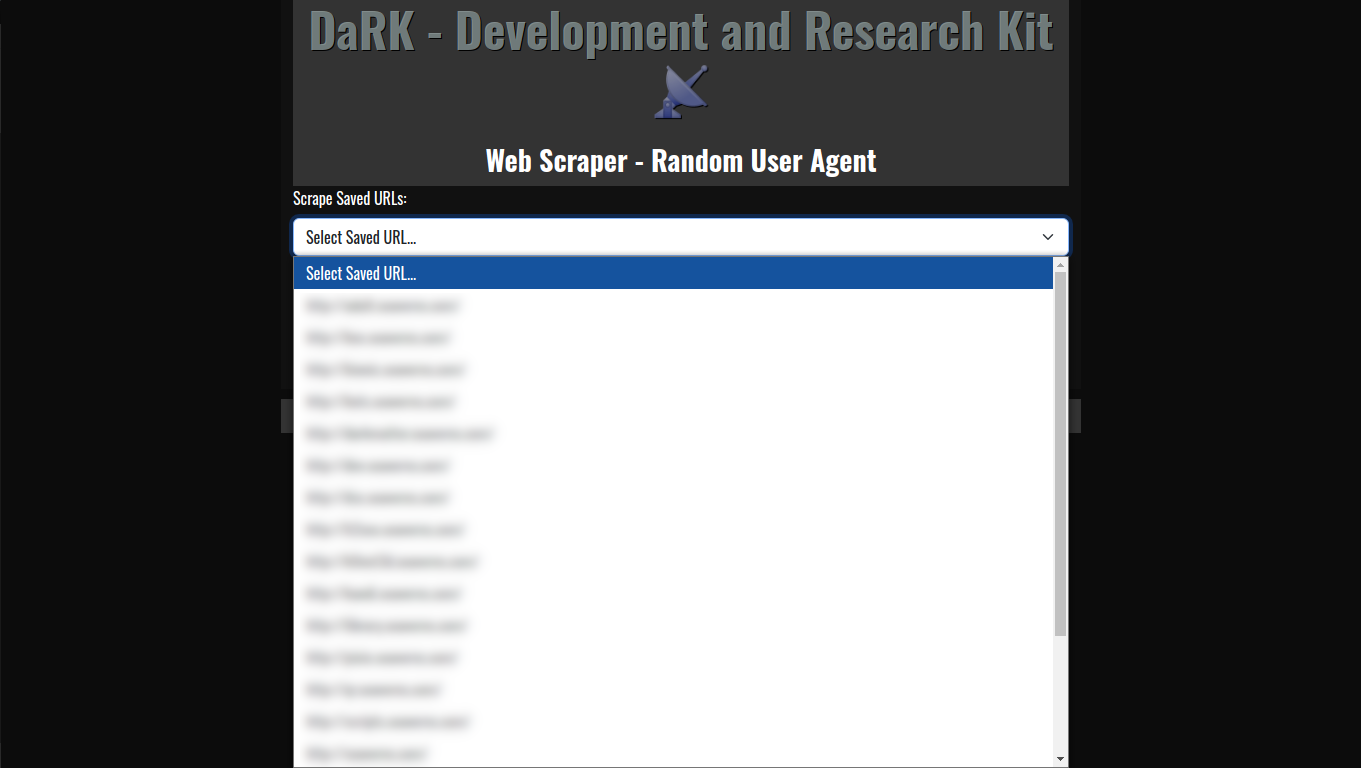
What Is A BotNet?
What Is A BotNet?
A botnet is a network of compromised computers or devices, often referred to as “bots” or “zombies,” which are controlled remotely by a cybercriminal or attacker. These bots are typically infected with malicious software (malware) that allows the attacker to take control of the infected devices without the owners’ knowledge.

BotNet CNC Control Hacker Inflitration Exploits Vulnerabilities SSH TCP Bots Hardware Software Exploited
Botnets can be used for various malicious activities, including:
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: The botnet can be used to flood a target server or website with traffic, overwhelming its resources and causing it to crash or become unavailable.
- Spam and Phishing Campaigns: Botnets can send out massive volumes of spam emails or phishing messages, often to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, or financial data.
- Data Theft: Attackers can use botnets to steal personal or financial data from infected devices, often through keylogging or other forms of surveillance.
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Cybercriminals can hijack the processing power of infected devices to mine cryptocurrencies, which can be highly profitable.
- Credential Stuffing: Botnets can automate the process of trying stolen usernames and passwords on various websites, attempting to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
Botnets can consist of hundreds, thousands, or even millions of infected devices, which makes them particularly powerful and difficult to combat. These devices can include computers, smartphones, IoT devices (such as cameras, smart thermostats, etc.), and more.
In some cases, botnet operators rent out or sell access to their botnets, allowing other criminals to carry out attacks for profit.
Botnets are illegal, and organizations and individuals need to protect their devices from becoming part of a botnet by using up-to-date antivirus software, firewalls, and practicing good cybersecurity hygiene.
What Is A BotNet?
A botnet works by infecting multiple devices (often referred to as “zombies” or “bots”) with malicious software (malware) and then allowing a central controller, known as the botmaster, to remotely command and control these devices. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a botnet typically operates:
1. Infection:
The process begins when a device is infected with malware that allows it to be controlled remotely. This malware can be spread through various methods:
- Phishing emails: Malicious links or attachments that, when clicked, install the malware.
- Exploiting software vulnerabilities: Malware can take advantage of unpatched security holes in operating systems, software, or applications.
- Malicious websites: Visiting a compromised website or one that hosts exploit kits can result in automatic malware downloads.
- Trojan horses: Software that pretends to be legitimate but secretly installs malware when executed.
- Social engineering: Convincing a user to download and install the malicious software themselves.
Once the malware is installed on the device, it connects back to the command-and-control (C&C) server controlled by the attacker.
2. Connection to the Command-and-Control (C&C) Server:
After infection, the bot establishes a connection to a central server (or a set of servers) controlled by the attacker. The C&C server sends commands to the infected devices, and the bots report back on their status.
- Centralized C&C: In a centralized botnet, all infected devices communicate with a single server controlled by the botmaster. The server sends commands and updates to the bots.
- Decentralized (P2P) C&C: Some advanced botnets use a peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture, where infected devices communicate directly with each other and distribute commands, making it harder to shut down the botnet.
3. Botnet Command Execution:
Once the bots are connected to the C&C server, the botmaster can issue commands that will be executed by all or selected infected devices. Some common commands include:
- DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service): Directing all infected bots to flood a target website or server with massive amounts of traffic, overwhelming it and causing it to go offline.
- Data theft: Commands to capture sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, or personal information.
- Spamming: Directing infected devices to send out large volumes of spam emails, often for the purpose of spreading malware or conducting phishing attacks.
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Instructing infected devices to perform resource-intensive mining operations for cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Monero.
- Credential stuffing: Using the bots to automatically try stolen login credentials on various websites in an attempt to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
4. Scalability:
Botnets can consist of hundreds, thousands, or even millions of compromised devices, making them highly scalable and difficult to stop. The botmaster can issue commands to any number of infected devices at once.
The scale and reach of the botnet often depend on how many devices it has infected, as well as the geographical distribution of those devices.
5. Obfuscation and Persistence:
Botnets are designed to be stealthy and persistent. They often use several techniques to avoid detection and removal:
- Encryption: Communications between the bots and the C&C server are often encrypted to prevent detection by network monitoring tools.
- Self-replication: Some botnets can spread themselves further, infecting new devices automatically and adding them to the botnet.
- Anti-analysis techniques: Botnet malware might check whether it’s running in a virtual machine or being analyzed by antivirus software before activating itself.
- Periodic updates: The botnet malware can be updated remotely to improve its stealth or add new capabilities.
6. Monetization:
The botmaster typically uses the botnet to carry out illegal activities for financial gain.
Some common monetization strategies include:
- Renting out the botnet: Cybercriminals may rent out the botnet to others for malicious purposes, such as launching DDoS attacks, spamming, or stealing data.
- Selling stolen data: If the botnet is stealing sensitive information, it can be sold on the dark web.
- Cryptocurrency mining: The botmaster may use the infected devices’ processing power to mine cryptocurrencies, which can be highly profitable.
- Ransomware delivery: The botnet can be used to distribute ransomware, which locks the victim’s data and demands a ransom for its release.
7. Challenges in Detection and Mitigation:
Botnets are difficult to detect and neutralize because:
- Distributed nature: Botnets rely on a large number of devices spread across many different networks, making it hard to target them all at once.
- Fast-flux: Some botnets use dynamic DNS techniques like “fast-flux” to constantly change their C&C servers’ IP addresses, making it hard for security researchers and authorities to track them down.
- Encryption: Botnet traffic is often encrypted, making it difficult for network monitoring tools to identify malicious activity.
- Diverse infected devices: Botnets can infect a wide variety of devices, including computers, smartphones, and IoT devices (such as smart cameras or routers), many of which may not have robust security protections.
8. Botnet Disruption and Defense:
Efforts to dismantle or disrupt a botnet generally include:
- Identifying and shutting down C&C servers: Law enforcement and security organizations can take down or seize the botmaster’s C&C infrastructure, disrupting the botnet’s operations.
- Botnet takedown operations: Organizations like Google, Microsoft, and cybersecurity firms sometimes work together to disrupt botnets by pushing out updates to the infected devices or issuing “sinkhole” commands.
- Botnet detection tools: Security solutions that identify botnet traffic, use machine learning models to spot anomalies, or look for common indicators of botnet activity.
9. Preventing Botnet Infections:
To avoid becoming part of a botnet:
- Keep software updated: Regularly update your operating system, software, and devices to fix security vulnerabilities.
- Use antivirus software: Use reliable antivirus or anti-malware programs to detect and block malicious software.
- Avoid suspicious links and attachments: Be cautious when opening unsolicited emails or clicking on suspicious links.
- Implement network security: Use firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor network traffic for signs of botnet activity.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): This adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts, making them harder to hijack even if your credentials are compromised.
A botnet operates by infecting many devices with malware and using them for malicious purposes, typically controlled by a botmaster. The botnet can be used for a variety of criminal activities, and its decentralized nature makes it a significant challenge for cybersecurity professionals to dismantle and stop.
What Is A BotNet?

A History of Botnets: From the Beginning to Today
Botnets have been a significant threat in the world of cybersecurity for nearly two decades. They have evolved in both sophistication and scale, becoming an increasingly dangerous tool for cybercriminals.
Here’s a history of botnets, from their earliest days to the most contemporary and infamous examples.
Early Days of Botnets (2000s)
1. Mafiaboy (2000)
- The First Notable DDoS Attack: Though not technically a botnet, the attack launched by a hacker known as “Mafiaboy” in 2000 is considered one of the first widely publicized DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks. It targeted Yahoo! and caused major disruptions to the website.
- The Botnet Evolution: While Mafiaboy didn’t use a botnet in the strictest sense, the attack showed the potential of using multiple systems in a coordinated way to bring down a large site. This laid the groundwork for future botnet-based DDoS attacks.
2. Rbot (2001)
- Early Malware: Rbot was one of the first examples of a botnet-building Trojan. It allowed cybercriminals to create and control a network of infected computers. Initially, it was used for remote access, data theft, and launching small-scale attacks, but the concept of botnets had now taken shape.
Rise of Large-Scale Botnets (Mid-2000s to 2010)
3. Storm Worm (2007)
- One of the First Major Botnets: The Storm Worm is one of the most infamous early botnets, with estimates suggesting that it controlled millions of computers at its peak.
- Propagation: The botnet spread via spam emails with malicious attachments that, when opened, would install the Storm Worm on the victim’s computer. It was also known for its resilience, constantly changing its C&C (command and control) server addresses, making it difficult to dismantle.
- Malicious Activities: The botnet was used for sending spam, launching DDoS attacks, and distributing other malware. It was one of the first examples of botnets as a service, with various cybercriminal groups renting it for attacks.
4. Conficker (2008)
- Massive Scale: Conficker was one of the largest and most successful botnets of its time. At its peak, it infected over 12 million computers worldwide.
- Self-Propagation: It spread through vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows (especially the MS08-067 vulnerability) and used advanced techniques to avoid detection and shut down.
- Complex Control: Conficker used a peer-to-peer (P2P) communication system to make it harder to locate and disrupt the C&C servers.
- Key Use: The botnet was involved in data theft, spam, and other criminal activities. While law enforcement and security organizations managed to mitigate it, Conficker left a lasting impact on cybersecurity awareness.
Modern Era of Botnets (2010–2019)
5. Zeus/Zbot (2007–2010s)
- Banking Malware: Zeus, also known as Zbot, was a sophisticated malware that targeted banking institutions to steal login credentials and financial data.
- Botnet Building: The malware was used to create one of the most prolific financial botnets in history. It employed advanced keylogging and form-grabbing techniques to steal sensitive financial information.
- Impact: Zeus was widely distributed and used in major cybercrimes, including identity theft, fraud, and even facilitating ransomware attacks.
- Adaptation: Zeus later evolved into more advanced versions like Zeus Panda and Gameover Zeus, making it more difficult to detect and shut down.
6. ZeroAccess (2011–2013)
- A Search Engine Hijacker: ZeroAccess was a large and versatile botnet that could be used for multiple malicious purposes. It primarily infected machines to use their processing power for click fraud and Bitcoin mining.
- Multi-Purpose Botnet: ZeroAccess was also involved in distributing malware and launching DDoS attacks, and it had a highly decentralized infrastructure that made it difficult to track.
- Botnet Takedown: In 2013, a collaborative effort by Microsoft, Europol, and other entities took down the core of the ZeroAccess botnet.
7. Mirai (2016)
- IoT-Based Botnet: One of the most infamous contemporary botnets, Mirai took advantage of the growing number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with weak security. These devices (like IP cameras, routers, and DVRs) were infected and turned into bots.
- Massive DDoS Attacks: The Mirai botnet launched some of the largest DDoS attacks in history, including the attack on Dyn, a major DNS provider, which caused widespread internet outages across the U.S.
- Innovation in DDoS: Mirai’s massive scale and its ability to use IoT devices demonstrated the potential for botnets to affect more than just computers and servers. The botnet also brought attention to the security vulnerabilities inherent in IoT devices.
Contemporary and Recent Botnets (2020–Present)
8. Emotet (2014–2021)
- Malware-as-a-Service: Initially emerging as a banking Trojan, Emotet evolved into a botnet-as-a-service, with other criminals renting its infrastructure to distribute additional malware, including ransomware (like Ryuk) and TrickBot.
- Widespread Infection: Emotet was responsible for the distribution of millions of phishing emails and malware payloads. It was very sophisticated, using multilayered attacks, often acting as a “loader” that installed additional threats on infected systems.
- Law Enforcement Takedown: In early 2021, law enforcement agencies, including Europol, launched an international operation to dismantle Emotet’s infrastructure, but its impact still resonates in the form of related ransomware groups.
9. TrickBot (2016–Present)
- Advanced Botnet: TrickBot is one of the most sophisticated and adaptable botnets in recent years. Originally focused on financial theft, it evolved into a modular botnet that also facilitated ransomware attacks and data theft.
- Ransomware Distribution: TrickBot is often used to deploy Ryuk ransomware or Conti ransomware after infiltrating corporate networks. It’s been linked to large-scale attacks against hospitals, universities, and businesses.
- Resilient Infrastructure: TrickBot uses a highly distributed and resilient infrastructure, with peer-to-peer communications between infected systems, which makes it challenging for authorities to take down.
- Takedown Efforts: A joint operation by the FBI, Microsoft, and international law enforcement agencies disrupted TrickBot’s operations in 2020, but the botnet is still active in modified forms.
10. Qbot (2008–Present)
- Persistent Threat: Qbot (also known as QuakBot) is another sophisticated botnet that has been operating for over a decade. It is often used to facilitate bank fraud, data theft, and ransomware attacks.
- Advanced Techniques: Qbot is known for using living-off-the-land techniques, blending in with legitimate traffic and utilizing social engineering tactics to spread. It has also been part of ransomware campaigns like Ryuk and Conti.
- Survival and Adaptation: Despite multiple takedown attempts, Qbot has shown remarkable resilience, continuously adapting its tactics and using multi-layered obfuscation to evade detection.
11. Mirai 2.0 (2020s)
- New IoT Botnets: After the release of the original Mirai botnet, several variants, including Mirai 2.0, have emerged, continuing the trend of exploiting weakly secured IoT devices for large-scale DDoS attacks.
- Increased Focus on IoT Security: As IoT devices proliferate, these botnets have become a growing concern. Many devices have weak security protocols, making them easy targets for attackers to compromise and add to botnets.
The Evolution and Future of Botnets

Botnets have evolved significantly over the past two decades, from simple Trojans to massive, distributed networks that can launch sophisticated attacks and steal sensitive data on a global scale. Early botnets like Storm Worm and Conficker laid the groundwork, while more recent botnets like Mirai, Emotet, and TrickBot demonstrate an ever-growing sophistication, often tied to organized cybercrime or nation-state actors.
Today, botnets target everything from computers to IoT devices, and the rise of ransomware-as-a-service and malware-as-a-service has made them even more dangerous. As IoT devices continue to proliferate, and with many having poor security, botnets are likely to remain a significant cybersecurity threat.