DaRK Development and Research Kit 3.0
DaRK – Development and Research Kit 3.0 [Master Edition]:
Revolutionizing Web Scraping and Development Tools
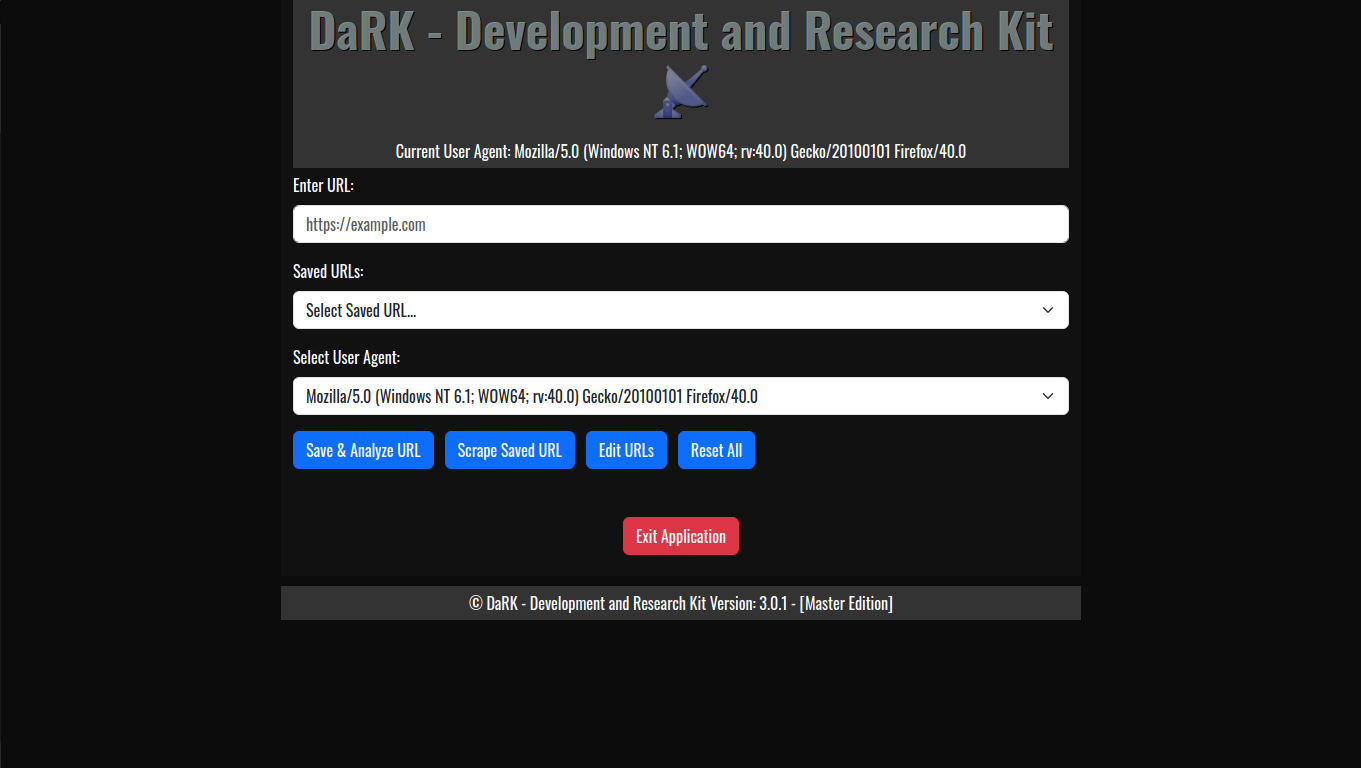
DaRK – Development and Research Kit 3.0 (Master Edition) is an advanced, standalone Python application designed for developers, researchers, and cybersecurity professionals. This tool streamlines the process of web scraping, web page analysis, and HTML code generation, all while integrating features such as anonymous browsing through Tor, automatic user-agent rotation, and a deep scraping mechanism for extracting content from any website.
Key Features and Capabilities
- Web Page Analysis:
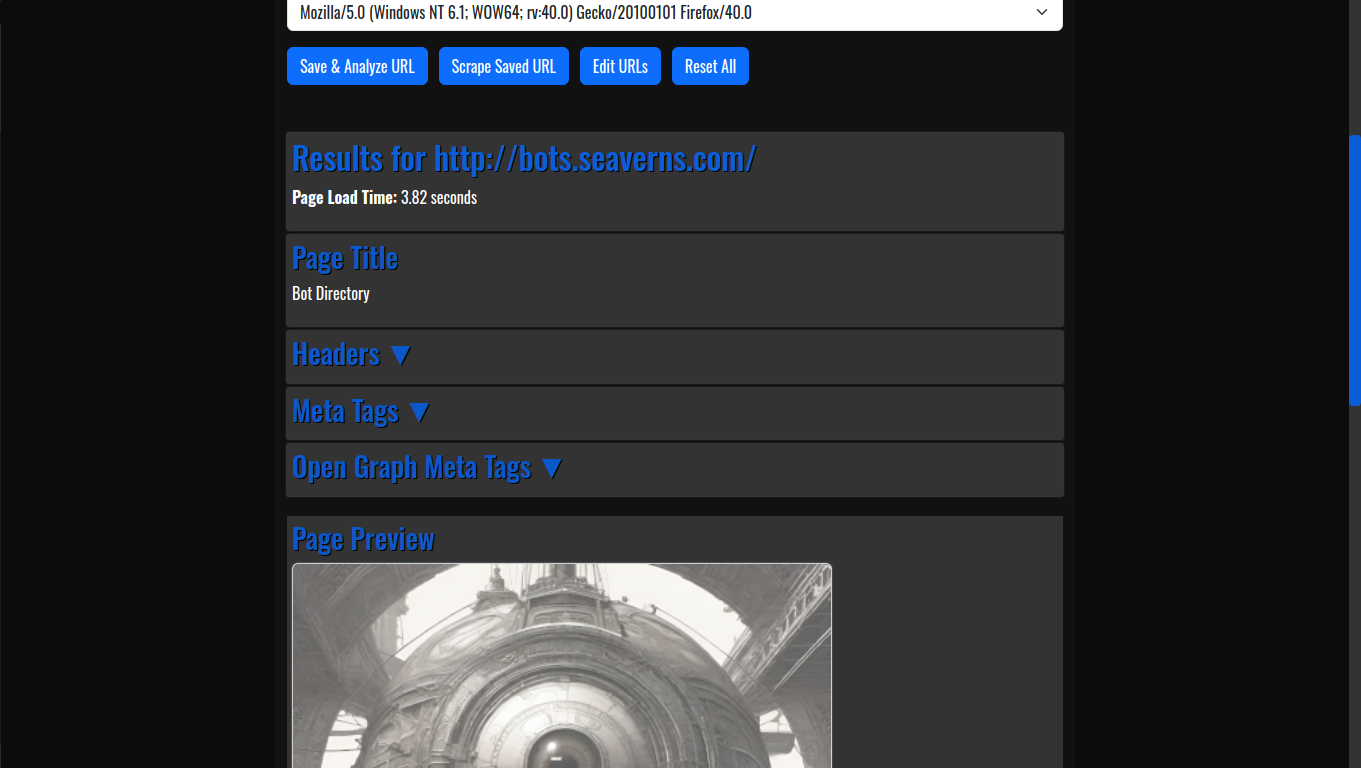
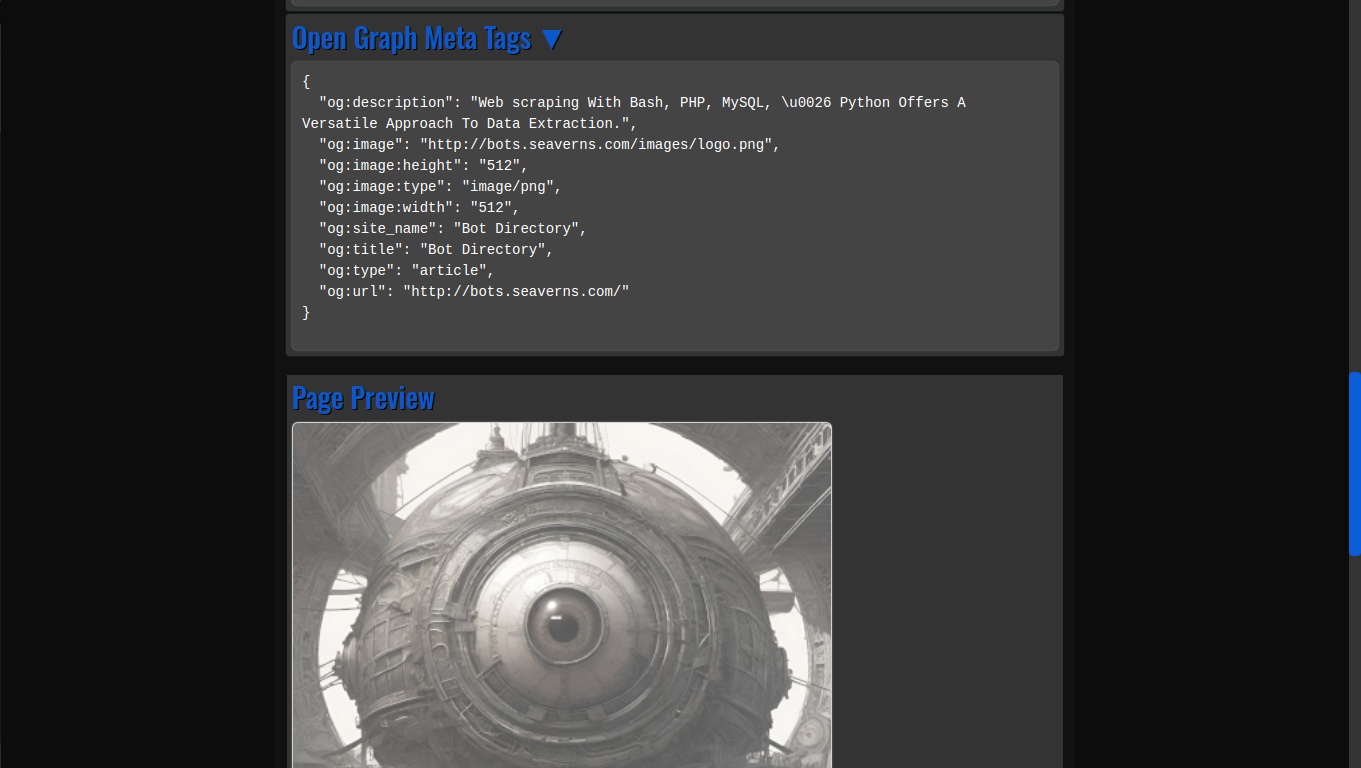
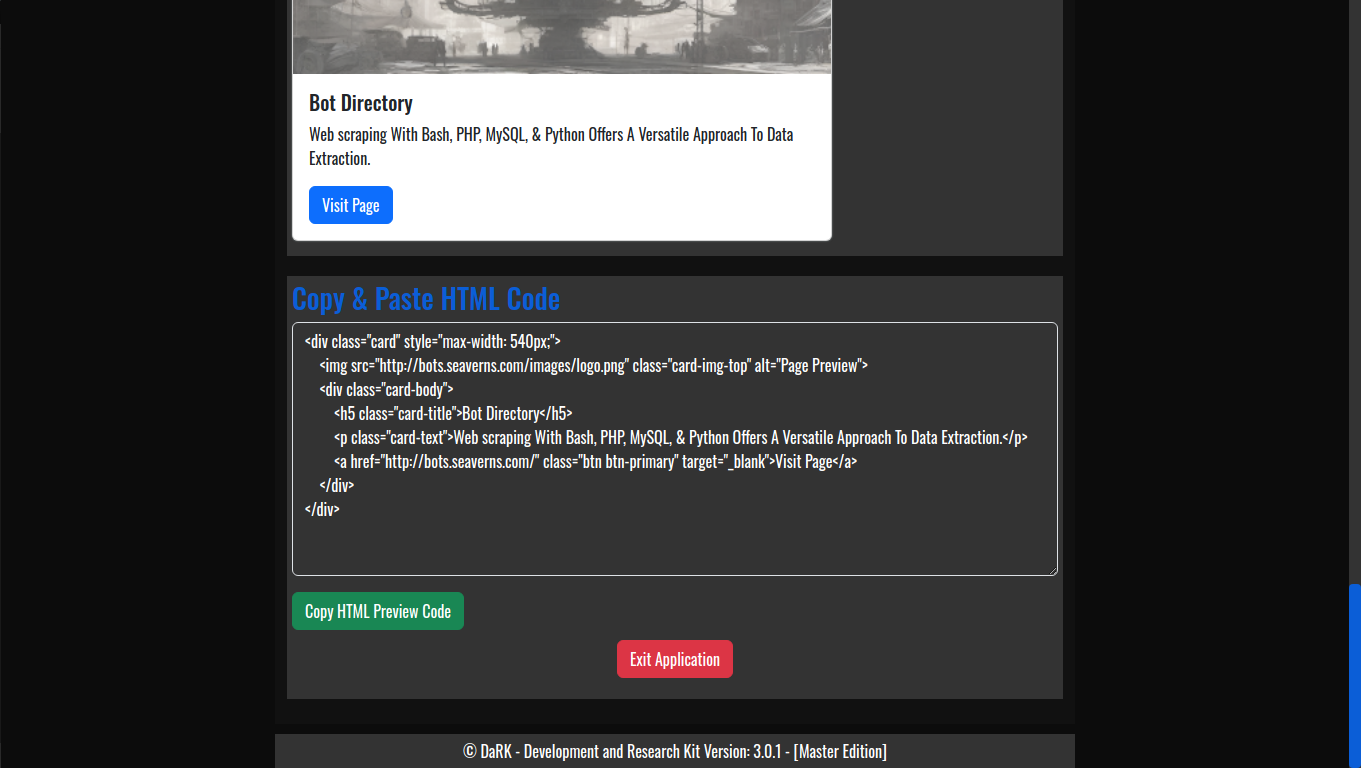
- HTML Code Previews: The application allows developers to generate live HTML previews of web pages, enabling quick and efficient testing without needing to launch full web browsers or rely on external tools.
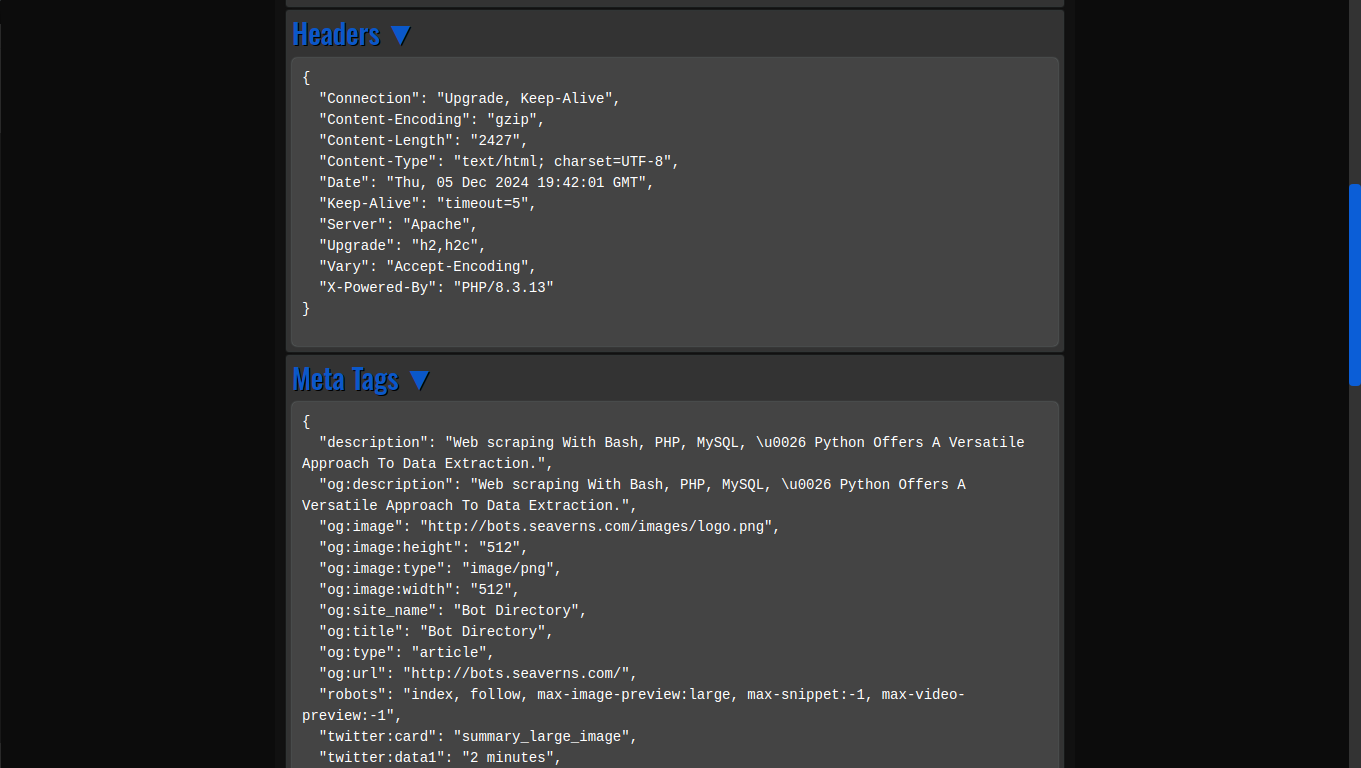
- View Web Page Headers: By simply entering a URL, users can inspect the HTTP headers returned by the web server, offering insights into server configurations, response times, and more.
- Og Meta Tags: Open Graph meta tags, which are crucial for social media previews, are extracted automatically from any URL, providing developers with valuable information about how a webpage will appear when shared on platforms like Facebook and Twitter.
- Web Scraping Capabilities:
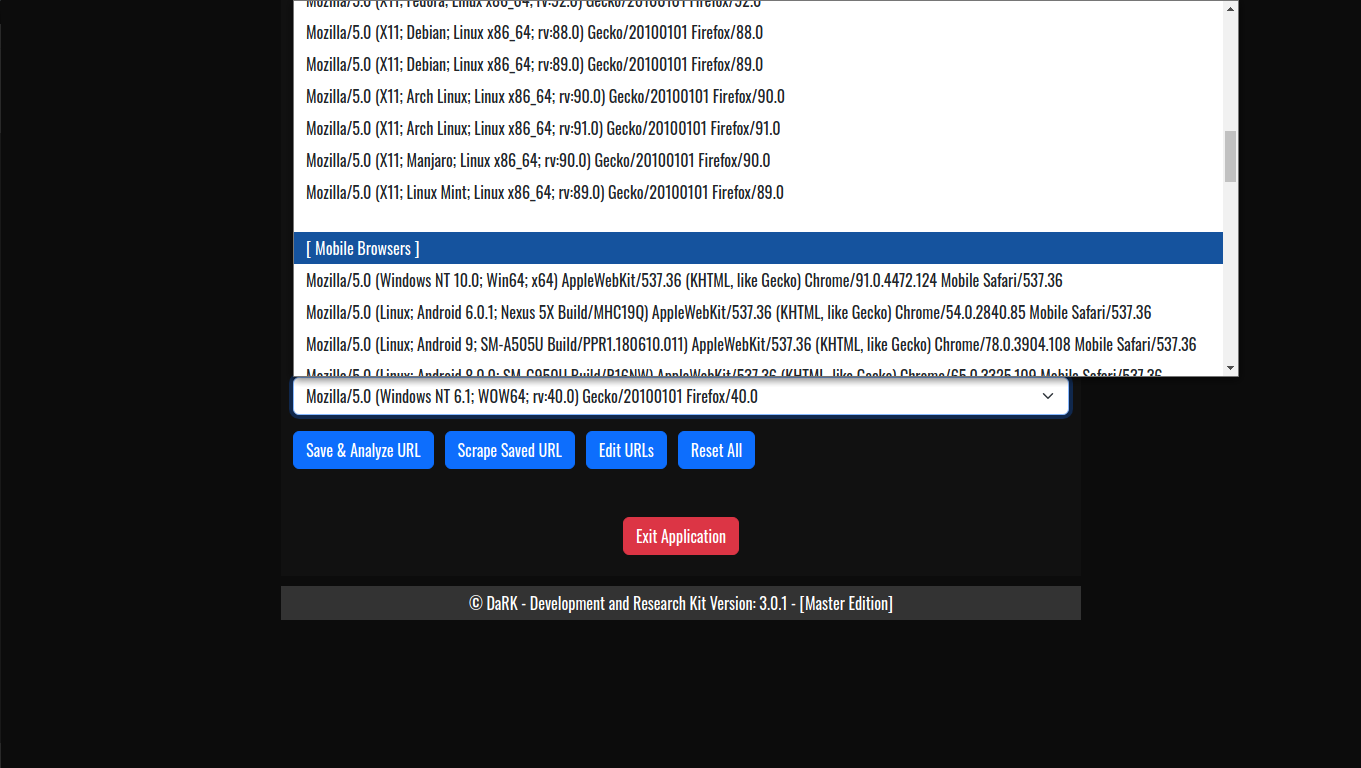
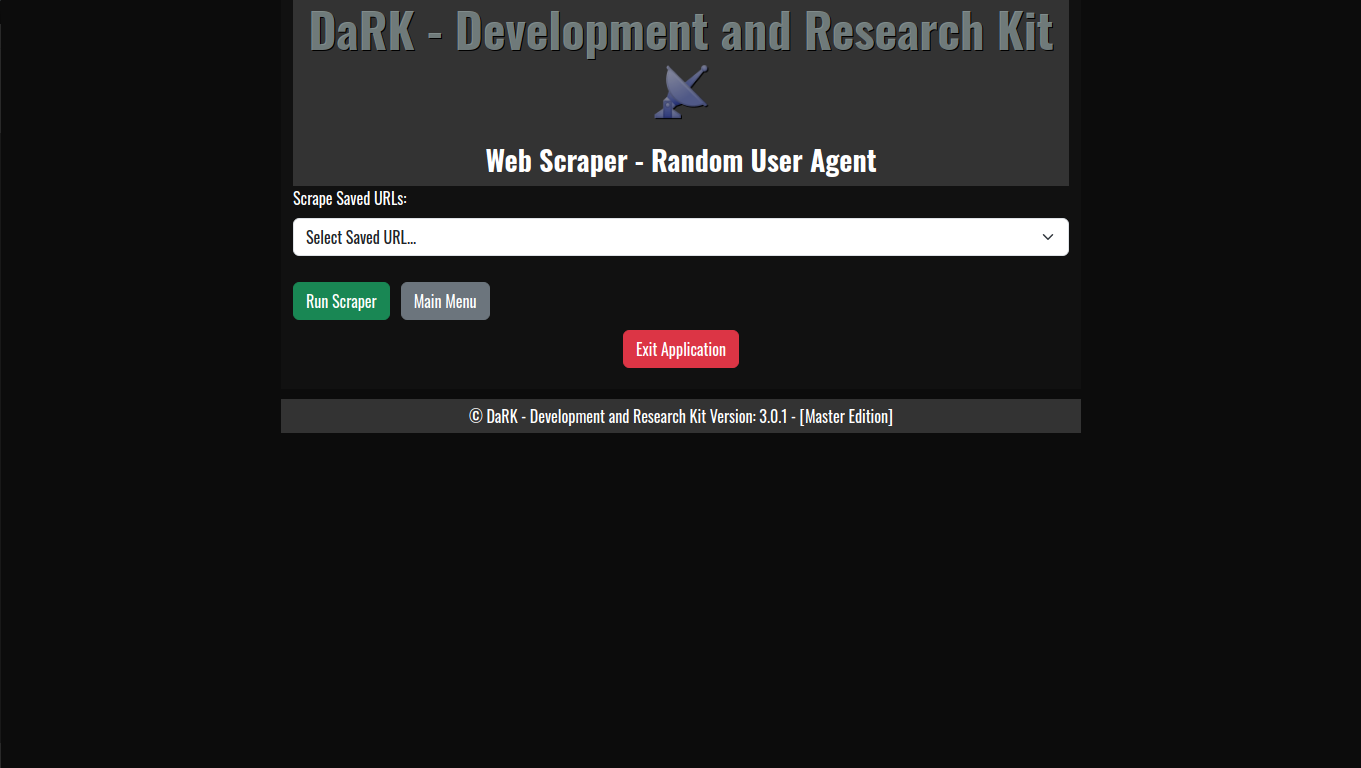
- Random User-Agent Rotation: The application comes with an extensive list of over 60 user-agents, including popular browsers and bots. This allows for a varied and random selection of user-agent strings for each scraping session, helping to avoid detection and rate-limiting from websites.
- Deep Scraping: The scraping engine is designed for in-depth content extraction. It is capable of downloading and extracting nearly every file on a website, such as images, JavaScript files, CSS, and documents, making it an essential tool for researchers, web developers, and penetration testers.
- Anonymity with Tor:
- The app routes all HTTP/HTTPS requests through Tor, ensuring anonymity during web scraping and browsing. This is particularly beneficial for scraping data from sites that restrict access based on IP addresses or are behind geo-blocking mechanisms.
- Tor Integration via
torsocks: DaRK leverages thetorsockstool to ensure that all requests made by the application are anonymized, providing an extra layer of privacy for users.
- Browser Control:
- Launch and Close Browser from HTML: Using the Chrome browser, DaRK can launch itself as a web-based application, opening a local instance of the tool’s user interface (UI) in the browser. Once finished, the app automatically closes the browser to conserve system resources, creating a seamless user experience.
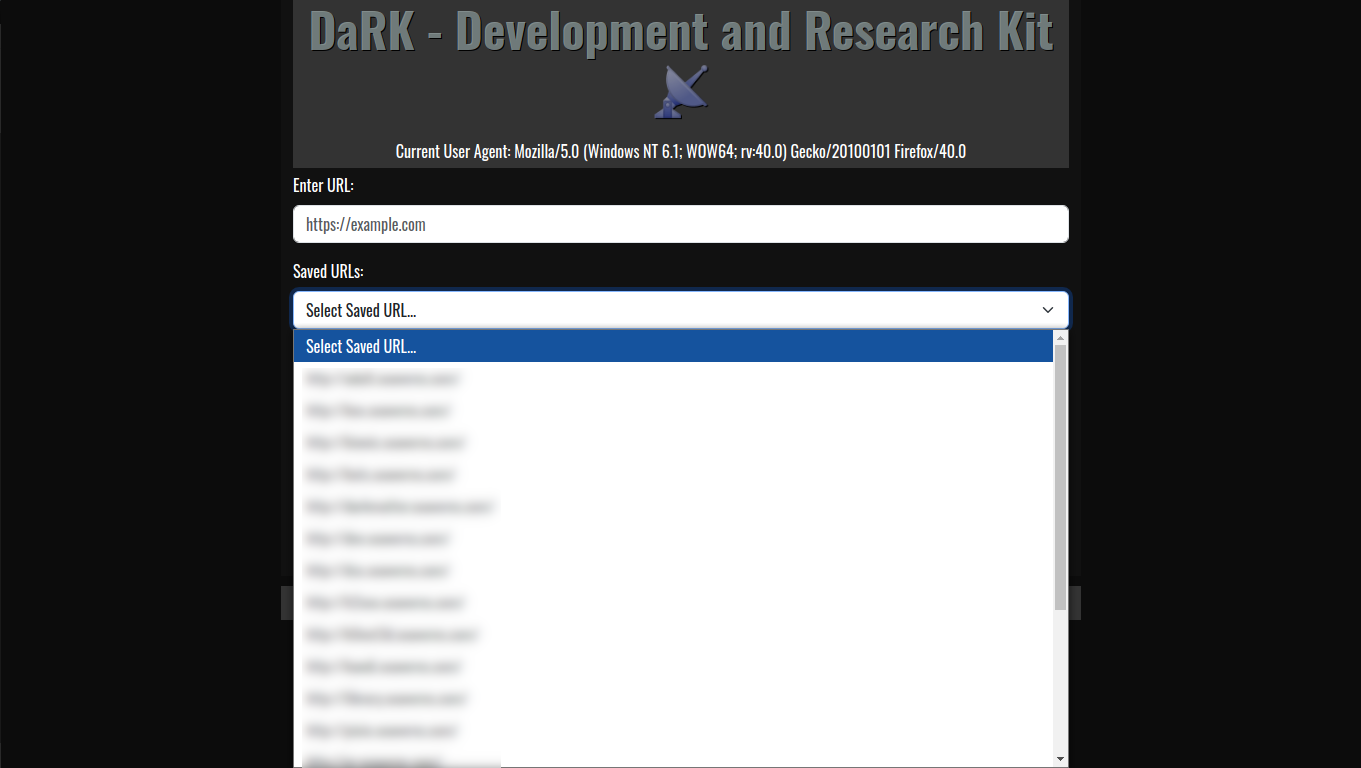
- SQLite Database for URL Storage:
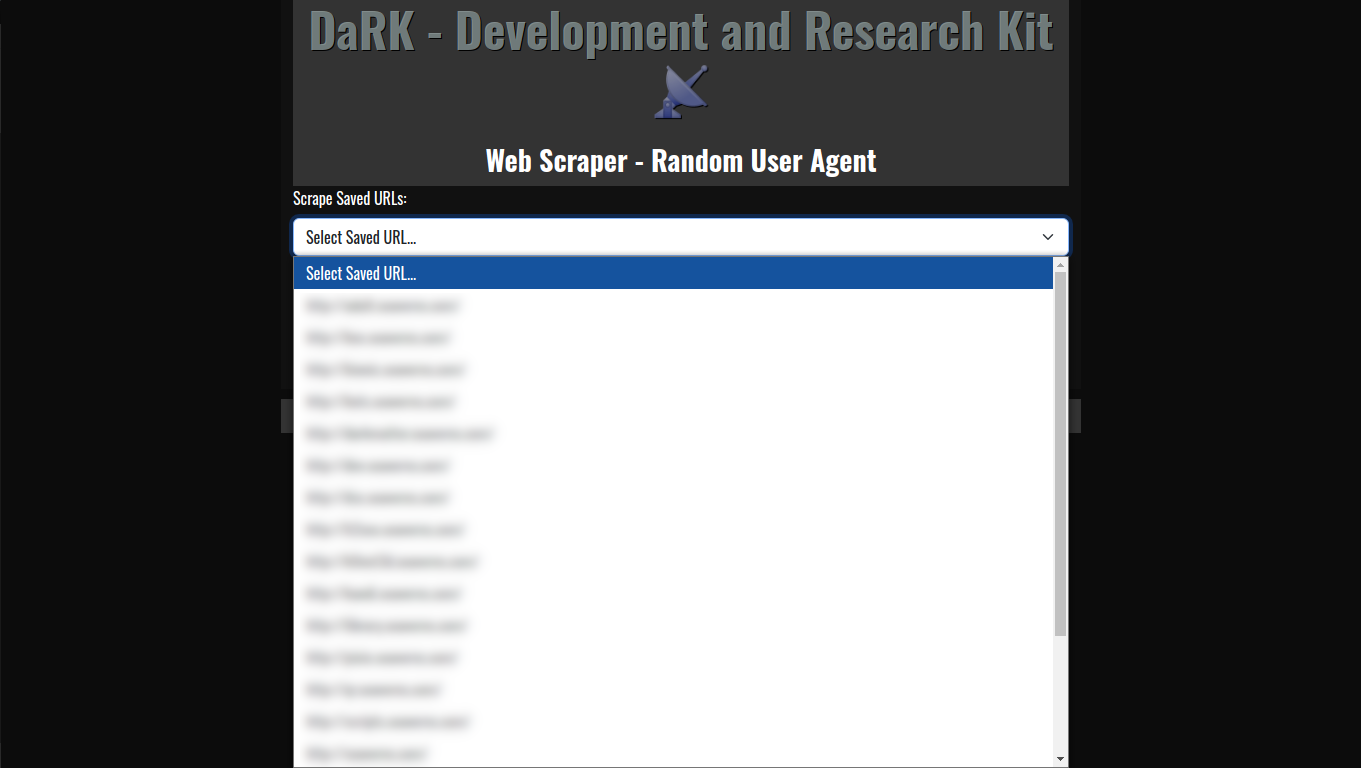
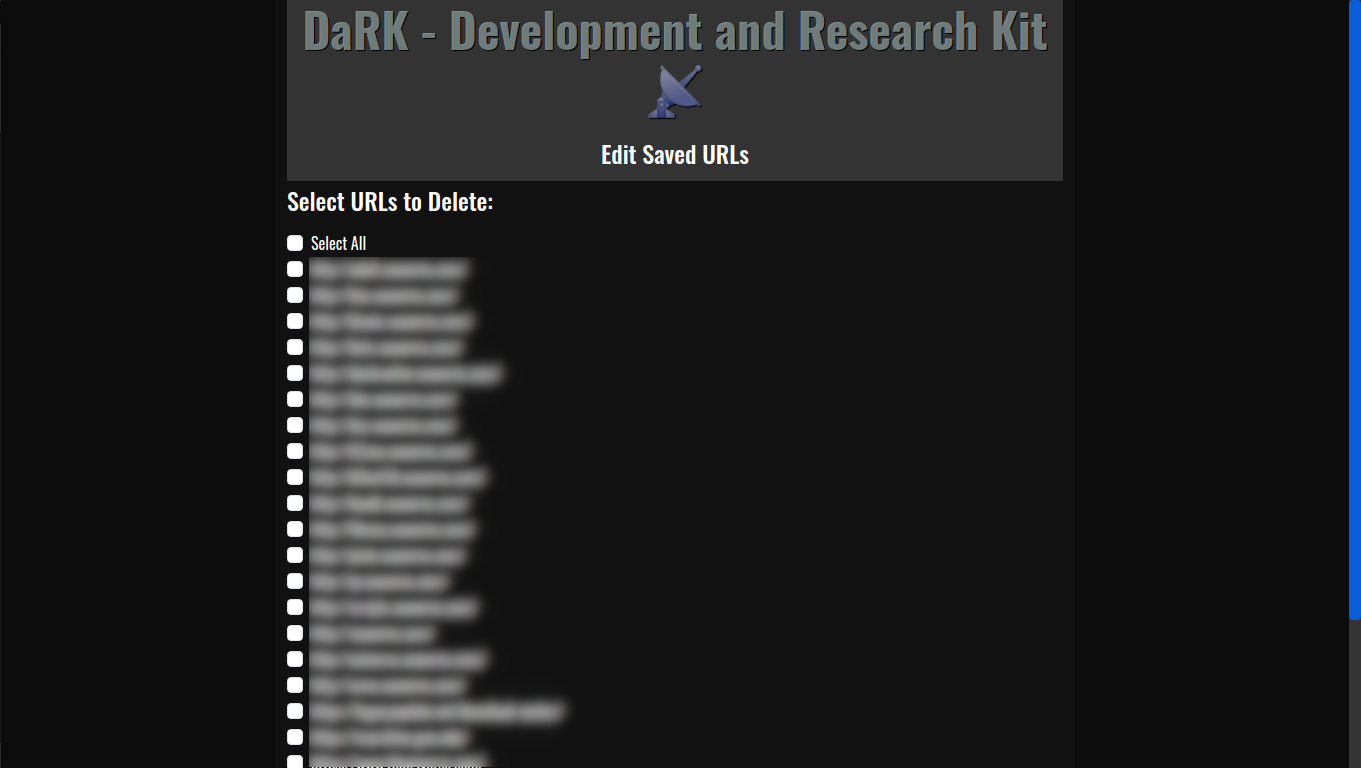
- Persistent Storage: The tool maintains a local SQLite database where URLs are stored, ensuring that web scraping results can be saved, revisited, and referenced later. The URLs are timestamped, making it easy to track when each site was last accessed.
- Flask Web Interface:
- The application includes a lightweight Flask web server that provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with the app. Users can input URLs, generate previews, and review scraped content all from within a web-based interface.
- The Flask server runs locally on the user’s machine, ensuring all data stays private and secure.
DaRK Development and Research Kit 3.0 Core Components
- Tor Integration: The
get_tor_session()function configures the requests library to route all traffic through the Tor network using SOCKS5 proxies. This ensures that the user’s browsing and scraping activity remains anonymous. - Database Management: The
initialize_db()function sets up an SQLite database to store URLs, andsave_url()ensures that new URLs are added without duplication. This enables the tool to keep track of visited websites and their metadata. - Web Scraping: The scraping process utilizes BeautifulSoup to parse HTML content and extract relevant information from the web pages, such as Og meta tags and headers.
- Multi-threading: The tool utilizes Python’s
ThreadandTimermodules to run operations concurrently. This helps in opening the browser while simultaneously executing other tasks, ensuring optimal performance.
Use Case Scenarios
- Developers: DaRK simplifies the process of generating HTML previews and inspecting headers, making it a valuable tool for web development and testing.
- Cybersecurity Professionals: The deep scraping feature, along with the random user-agent rotation and Tor integration, makes DaRK an ideal tool for penetration testing and gathering information on potentially malicious or hidden websites.
- Researchers: DaRK is also an excellent tool for gathering large volumes of data from various websites anonymously, while also ensuring compliance with ethical scraping practices.
DaRK Development and Research Kit 3.0
DaRK – Development and Research Kit 3.0 [Master Edition] is a powerful and versatile tool for anyone needing to interact with the web at a deeper level. From generating HTML previews and inspecting web headers to performing advanced web scraping with enhanced privacy via Tor, DaRK offers an all-in-one solution. The application’s integration with over 60 user agents and its deep scraping capabilities ensure it is both effective and resilient against modern web security mechanisms. Whether you are a developer, researcher, or security professional, DaRK offers the tools you need to work with the web efficiently, securely, and anonymously.