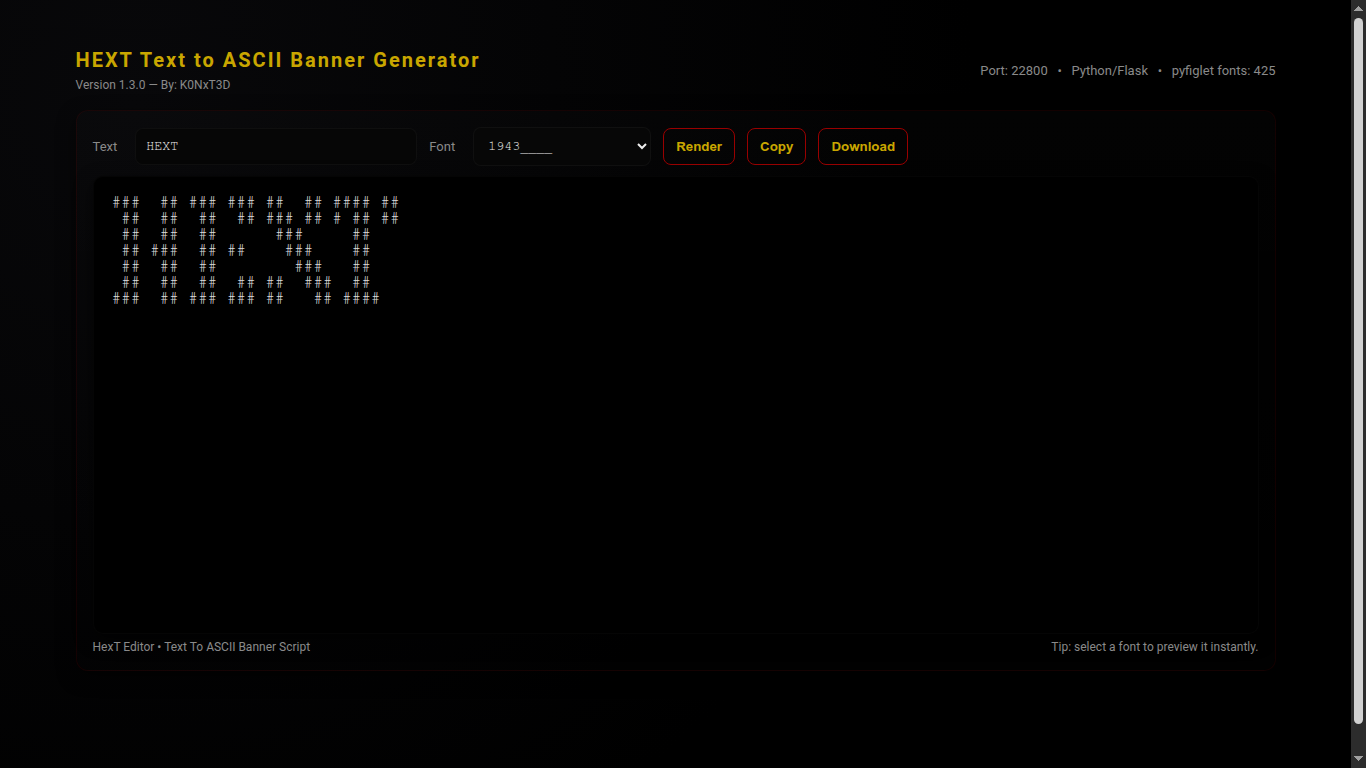
HEXT 2.0 Text to ASCII Banner Generator
HEXT 2.0 Text to ASCII Banner Generator
HEXT 2.0 Text to ASCII Banner Generator is a Python3 web application that converts text into ASCII banners using pyfiglet.
It features a modern, dark aesthetic interface with live font selection, copy and download functionality, and full-screen previews.
Version Information
Version: 2.0
Author: K0NxT3D
Website: seaverns.com
Download
Core Features
🖋 Text to ASCII
- Render text using any installed pyfiglet font
- Live preview with instant updates
- Copy to clipboard or download as .txt
🎨 Font Selection
- Dropdown menu for all available pyfiglet fonts
- Sidebar font reference panel
- Dynamic highlighting of selected font
💻 Web Interface
- Dark hacker aesthetic layout
- Responsive design for desktop and mobile
- Clean two-column layout with sidebar
Requirements
- Python 3.12+ (tested on Ubuntu 24 & Raspberry Pi)
- pip3 installed
Python Packages
- Flask ≥ 2.3.2
- pyfiglet ≥ 0.8.post1
Installation
cd HEXT python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate pip install -r requirements.txt python3 hext.py
Usage
1) Launch Application
python3 hext.py
2) Open in Browser
http://127.0.0.1:22800/
3) Enter Text & Render
- Type text into the input field - Select a font from the dropdown - Click "Render"
4) Copy / Download
- Click "Copy" to clipboard - Click "Download" to save .txt file
License
MIT License Copyright (c) 2025 Rob Seaverns Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.