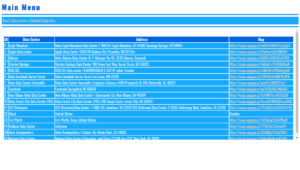
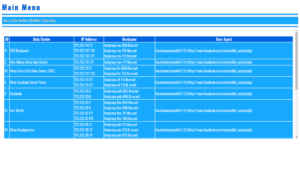
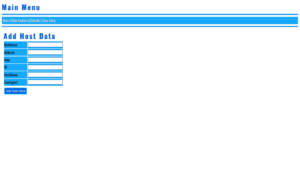
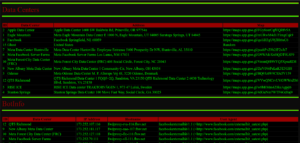
OpenSSL Encryption and Decryption
Unveiling the Secrets: OpenSSL Encryption and Decryption with Session Data vs. MySQL Storage Through the Lens of Sun Tzu
In the digital battlefield, securing data is paramount. OpenSSL encryption and decryption are crucial weapons in our arsenal, and understanding the strategic use of session data (cookies) versus MySQL storage can make all the difference. To explore these strategies, we’ll turn to the ancient wisdom of Sun Tzu’s “The Art of War,” examining the strengths and weaknesses of these approaches and how they align with Sun Tzu’s principles.
The Battlefield: OpenSSL Encryption and Decryption
OpenSSL is a robust toolkit that provides cryptographic functions, including encryption and decryption. Its strength lies in its ability to secure data using algorithms like AES-256, combined with mechanisms such as initialization vectors (IVs) and hash-based message authentication codes (HMACs). But where should this encryption and decryption take place? In the realms of session data or database storage?
Session Data (Cookies): The Quick Strike
1. The Strategy of Speed and Agility
- Convenience: Storing encryption keys or encrypted data in session cookies offers swift access and ease of implementation. This is akin to a swift cavalry maneuver, allowing for rapid deployment and access to encrypted data.
- Stateless Operations: Sessions offer a temporary battlefield, where data and keys are managed on a per-session basis. This approach allows for quick encryption and decryption but limits the persistence of data to the lifespan of the session.
2. The Risks of the Quick Strike
- Security Risks: Session cookies are stored on the client-side, making them vulnerable to attacks such as cross-site scripting (XSS). The strategic challenge here is to safeguard the session data as it traverses the battlefield.
- Limited Persistence: Once the session ends, so do the cookies, making this strategy less suitable for long-term data storage.
Sun Tzu’s Wisdom: “Speed is the essence of war.” The agility of session storage aligns with this principle, offering rapid access but at the cost of security and persistence.
MySQL Storage: The Strategic Fortification
1. The Strategy of Long-Term Security
- Persistent Storage: MySQL databases provide a secure, long-term storage solution for both encryption keys and encrypted data. This is like fortifying a stronghold, ensuring data remains secure even beyond the immediate campaign.
- Controlled Access: By keeping sensitive information on the server-side, you reduce exposure to client-side attacks. This strategy is more resilient to external threats.
2. The Risks of Fortification
- Performance Overhead: Accessing and managing data in MySQL can introduce latency compared to session storage. This is akin to the slower movement of a fortified army compared to a fast-moving cavalry.
- Complexity: Implementing encryption and decryption with MySQL involves additional complexity, such as handling database connections and ensuring robust security measures for stored data.
Sun Tzu’s Wisdom: “The skillful fighter puts himself into a position which makes defeat impossible.” Using MySQL for secure storage aligns with this principle, ensuring long-term security and control, albeit with a potential trade-off in agility and performance.
Comparative Analysis
1. Security and Persistence
- Session Data: Offers immediate access but with higher risks and lower persistence. Ideal for temporary or ephemeral data needs.
- MySQL Storage: Provides persistent and secure data storage but with added complexity and potential performance costs. Suitable for long-term data management.
2. Flexibility vs. Fortification
- Session Data: Flexibility and speed in data handling, akin to a quick strike on the battlefield. However, security and persistence are not as fortified.
- MySQL Storage: Fortified and secure, but potentially slower and more complex to manage. A strategic choice for long-term data protection.
Sun Tzu’s Wisdom: “Know your enemy and know yourself and you can fight a hundred battles without disaster.” Understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach allows you to choose the best strategy for your specific needs.
Examples:
- OpenSSL Encryption/Decryption Using Stored Session Data (Cookies) Demo
- OpenSSL Encryption/Decryption Using Random Cyphers & Stored Session Data (Cookies) Demo
Conclusion
In the realm of data encryption and decryption, the choice between session storage and MySQL storage reflects a balance between speed, security, and persistence. Like Sun Tzu’s strategic principles, your approach should be guided by the context and objectives of your mission. Whether you opt for the agility of session data or the fortification of MySQL, aligning your strategy with your needs ensures a victorious outcome in the ever-evolving landscape of digital security.
By applying these ancient strategies to modern encryption practices, you can better navigate the complexities of data security, ensuring that your digital battlefield is well-defended and strategically sound.